Ransomware was and still is one of the most dangerous attacks that can cause catastrophic consequences to the endpoint system if not responded properly. The following article is specially created for preparing incident response teams against this particular attack, but it is generally excellent guidance for everyone who would like to have clear and step-by-step approach on how to prepare, identify, contain, remediate and recover from the dangerous attacks of ransomware.
The following is part one of the overall incident response plan where we are going to discuss in our opinion the most critical phases of the incident response plan, which are the preparation and identification phases, because our goal is to prevent the compromise rather than allow it to be executed and completed, hence we will concentrate more on the phases mentioned above, but as well as we will cover other phases in part two and part three which are important as well. Before jumping into the phases and steps we would like to give brief introduction about ransomware, to explain what it is and how does it work.
Ransomware is a type of malware from crypto virology that threatens to publish the victim’s data or perpetually block access to it unless a ransom is paid. While some simple ransomware may lock the system in a way which is not difficult for an expert to reverse, more advanced malware uses a technique called crypto viral extortion, in which it encrypts the victim’s files, making them inaccessible, and demands a ransom payment to decrypt them.
In a properly implemented crypto viral extortion attack, recovering the files without the decryption key is an intractable problem and difficult to trace digital currencies such as Ukash or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency are used for the ransoms, making tracing and prosecuting the perpetrators difficult. As was already said we will divide the incident response plan into 5 phases and first phase is preparation from we shall start.
Preparation Overview:
On the preparation phase the company or the incident response team must realize that malicious actors often use phishing to infect a system with ransomware, hence it is very important to have a phishing policy. The chance of being compromised by ransomware can be decreased by conducting routine phishing tests, so employees will be able to detect a phishing email before clicking on any dangerous links or attachments.
To be ready for potential attacks such as ransomware the systems must be updated including the software with the latest security patches. This critical preventative step will make it harder for malicious actors to compromise your system. As ransomware became one of the most used and dangerous attack in a manner of data loss and system corruption, the company or the incident response team must prioritize the data that is most critical to the organization and back it up.
The recommended practice for backup is to periodically test the backups and verify the validity and reliability of the backups. For being ready and prepared there is yet another crucial step to cover to stay on the safest side and that is to deploy preventive cybersecurity resources. This can range from an anti-malware solution that includes endpoint or heuristic monitoring to advanced EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response) solution. Compared to the traditional anti-virus solutions which only detects malware at a signature level which can be ineffective in case of a new-born ransomware. Hence, we must implement advanced threat detection systems for cyber security resilience. The company or the incident response team should develop an incident response (IR) plan that is created specifically for a ransomware attack. It is crucial to prepare for targeted attacks that can affect broad swaths of your company.
The IR plan should detail the specific actions that specific people should take as soon as it becomes clear that an attack is on the way. This will help to ensure a quick and reactive response in a situation where time is limited of the essence to stop or contain a serious situation. Likewise, you should develop a disaster recovery plan specific to this type of attack. Major step that will let the company or the incident response team to navigate easily within identification phase is to identify and note all services and applications installed and used on the IT environment by profiling them and identifying how it is used and by which users, this step will allow us to quickly identify and profile any malicious activity.
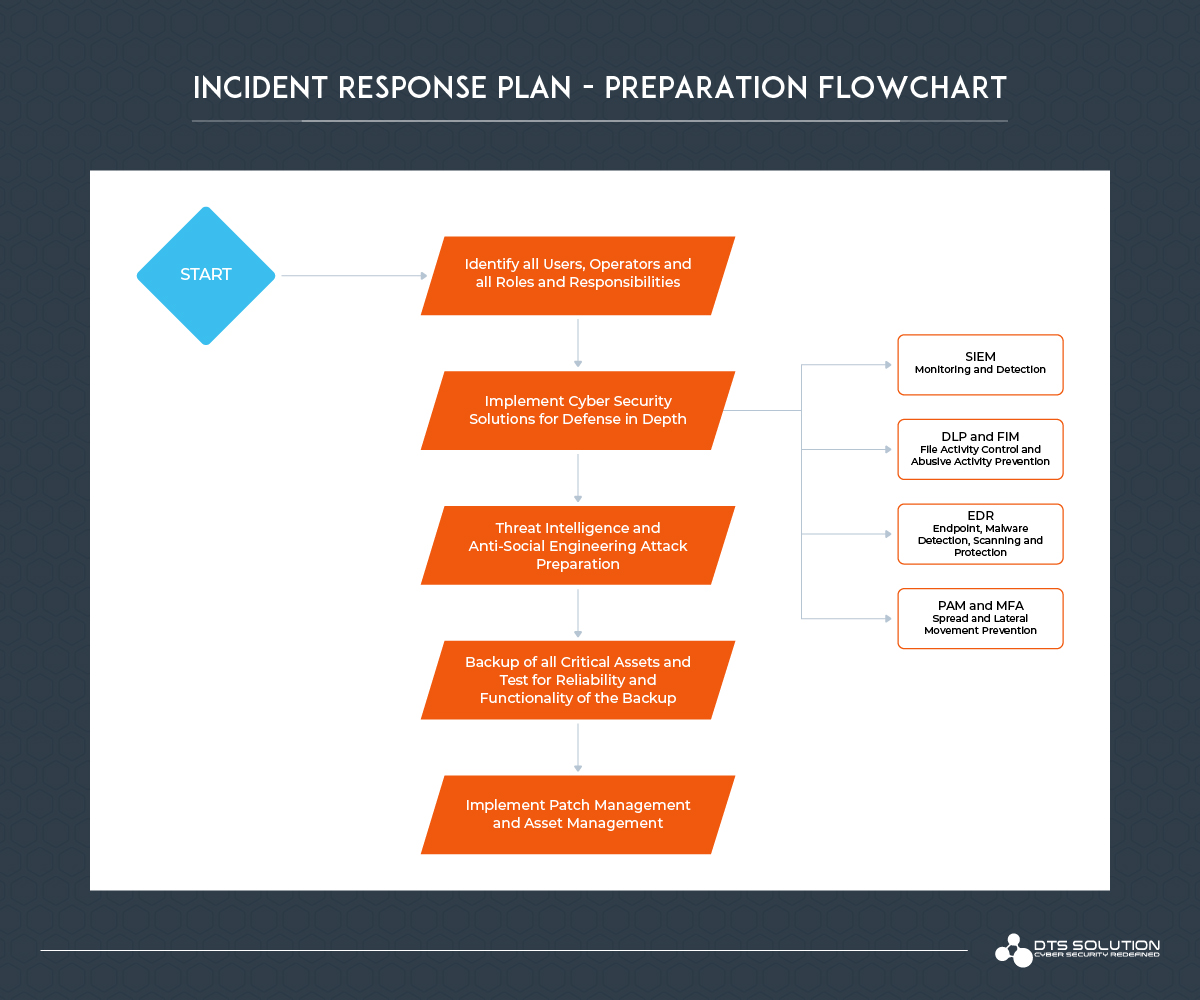
Preparation Hands-On:
- Identify all users, operators, teams, titles, positions, and main tasks including all roles and responsibilities.
- Implement cyber security solutions such as (EDR, PAM, MFA, LAPs, DLP, FIM, IDS/IPS, Anti-Virus/Anti-Spyware, SIEM etc.) for defense in depth.
- EDR, IDS/IPS, Anti-Virus/Spyware – For automated malware detection and prevention through quarantine mechanisms. Early detection and alert mechanisms to be able to respond quickly to already known malwares or ransomware.
- PAM and MFA – For prevention of privilege escalation and compromise of accounts which will let to access to confidential or restricted resources and encrypt or compromise them as well
- SIEM – Excellent visibility to overall infrastructure which will give the ability to monitor and control overall activities and network traffic that proceeds in your environment. This is done through the SIEM solution which collects all possible logs and through proper rules and dashboards visualizes the logs into meaningful data that can help to identify incident.
- DLP and FIM – For prevention of abusive/suspicious/malicious file transfer, file creation, file deletion or modification.
- Ensure that you have the ability to:
- Raise personnel awareness
- Make report in case suspicious activity
- Set up relevant data collection
- Set up a centralized long-term log storage
- Develop communication map
- Make sure there are backups
- Get network architecture map
- Get access control matrix
- Develop assets knowledge base
- Check analysis toolset
- Access vulnerability management system logs
- Connect with trusted communities
- Access external/internal network flow logs
- Access internal HTTP logs, internal DNS logs, external HTTP logs
- Concentrate on anti-social engineering solutions by:
- Performing checks and scans on email attachments and ensure that you are able to do the following tasks quickly in order to remediate malicious activities in later steps.
- Ensure the ability to block external IP address, external URL, external domain
- Ensure the ability to list users opened email message
- Ensure the ability to list email message receivers
- Ensure the ability to block email domain, email sender
- Ensure the ability to delete/quarantine email message
- Employee training and cyber education
- Establishment of phishing policy
- Phishing tests on employees for validation that employees are able to response effectively to the attack (Not only IT team)
- Performing checks and scans on email attachments and ensure that you are able to do the following tasks quickly in order to remediate malicious activities in later steps.
- Perform perioding backups of all critical systems and most importantly test the backups for validity and reliability.
- Implement patch management and asset management.
- Consolidate all steps into one single effective incident response plan and create teams for that particular use case.
Identification Overview:
For initial identification and detection, a good approach is to get signatures and IOCs into your IDS. It is highly recommended as a best practice to use a threat intelligence sources to block and alert on the presence of anomalies that have a chance of being associated with ransomware in your network traffic. There are numerous signatures for most of the popular ransomwares out there such WannaCry and NotPetya traffic. These practice alone will not protect you from a ransomware because ransomwares can be modified and changed hence, we want to have more defense than just the detection. However, these signatures can be a useful source for the most widely distributed tools that enterprises tend to use.
Perform continuous anti-virus and overall endpoint security scans, to detect and discover unusual registry keys, malicious files, encrypted data, unusual directories, unusual amounts of internet traffic flow, unexplained system crashes, unauthorized and unexplained installation of software. Check the anti-virus notifications, scans, and Windows Event Logs for more details about the malicious activity. Request system updates and patches.
In case of phishing emails that may contain or lead users to the ransomware, the company or the incident response team must use tools that detect malicious attachments or perform attachment scanning to look for malicious attachments. This technique is your best automated defense against ransomware emails.
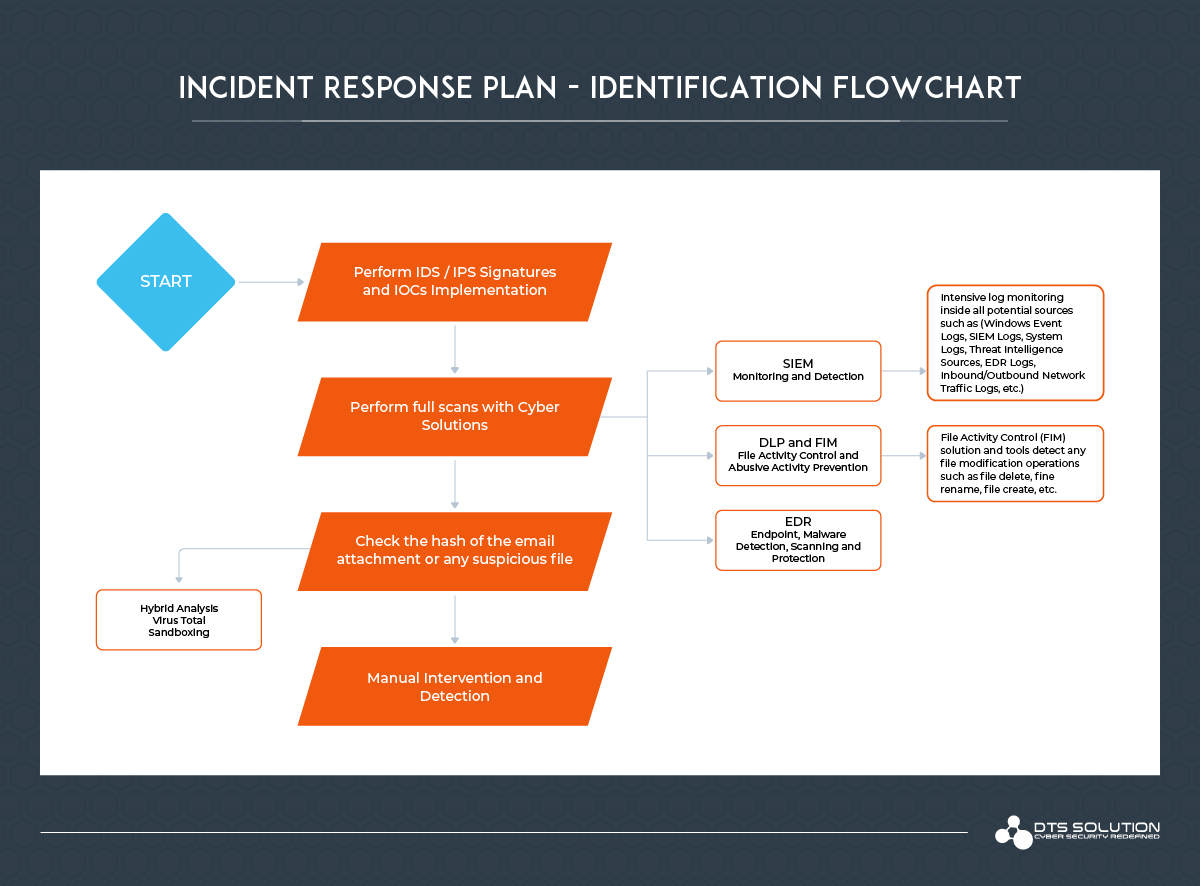
Identification Hands-On:
- Perform IDS/IPS Signatures and IOCs implementation, and check threat intelligence sources to detect anomalies and alert.
- Perform full scans with cyber solutions (Anti-Virus Scans, EDR Scans, Email Attachment Scans)
- Check the hash of the email attachment or any suspicious file, perform multiple anti-virus software scans, to ensure that the hash is malicious is in other AV databases as well for example Virus-Total.
- We must understand that one of the main sources of ransomware delivery is through email attachments, hence we need to have excellent monitoring on this process as well as cyber solutions to prevent any malicious activity.
- Manual intervention by checking and identifying any unusual registry keys, malicious files, encrypted data, unusual amount of interned traffic flow, unexplained system crashes, unauthorized and unexplained installation of software, not whitelisted applications, or files.
- By using File Activity Monitoring (FIM) solution and tools detect any file modification operations such as file delete, file rename, file create and etc.
- Intensive log monitoring inside all potential sources such as (Windows Event Logs, SIEM Logs, System Logs, Threat Intelligence Sources, EDR Logs, Inbound/Outbound Network Traffic Logs etc.)
- Manual intervention (Can be done automatically as well) to identify potential threats and affected assets or users by:
- Put compromised accounts on monitoring
- List hosts communicated with external IP, external URL, external domain
- List users opened email message
- Collect email message
- List email message receivers
- Make sure email message is phishing
- Extract observables from email message
This post is written by Armen Avagyan, Cyber Security Analyst at DTS Solution